Polar and nonpolar molecules pogil answers are at the heart of this exploration, where we delve into the fascinating world of molecular polarity. This comprehensive guide unravels the concepts, properties, and interactions of polar and nonpolar molecules, providing a deeper understanding of their significance in various scientific fields.
From the fundamental definitions of polarity to their impact on physical properties and intermolecular forces, we uncover the intricate relationships that govern the behavior of these molecules. By examining real-world applications and case studies, we gain insights into the practical implications of polarity in diverse industries.
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules: Definitions
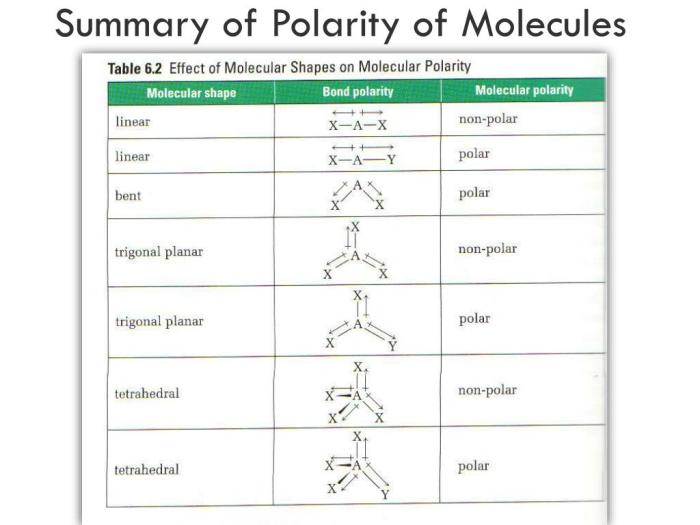
Polarity in molecules refers to the uneven distribution of electrons, resulting in a separation of positive and negative charges. Polar molecules possess a permanent dipole moment, while nonpolar molecules have no net dipole moment.
Examples of polar molecules include water (H 2O) and ammonia (NH 3), where the electronegative atoms (oxygen and nitrogen) attract electrons more strongly than the hydrogen atoms. Nonpolar molecules, such as methane (CH 4) and carbon dioxide (CO 2), have symmetrical electron distributions with no net charge separation.
The polarity of a molecule is influenced by its molecular structure, particularly the electronegativity of the atoms involved and the geometry of the molecule.
Properties of Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
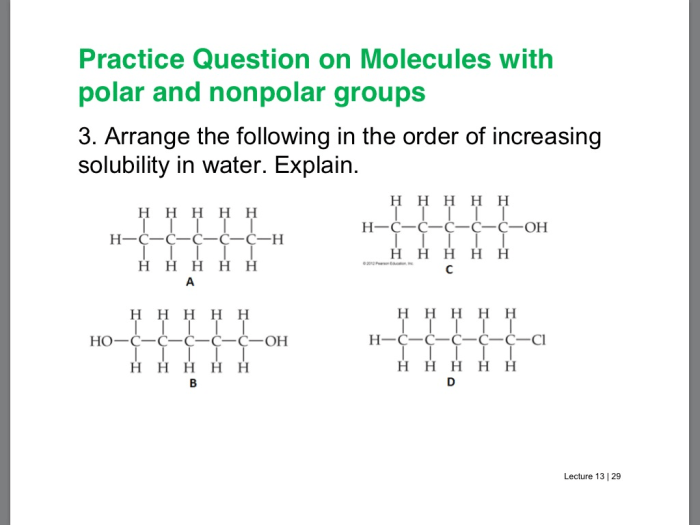
Physical Properties, Polar and nonpolar molecules pogil answers
Polar molecules tend to have higher boiling points and melting points compared to nonpolar molecules. This is because polar molecules experience stronger intermolecular forces, such as dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding, which require more energy to overcome.
Polar molecules are also more soluble in polar solvents, while nonpolar molecules are more soluble in nonpolar solvents. This is because “like dissolves like,” and the polarity of the solvent matches the polarity of the solute.
Behavior in Different Environments
The polarity of molecules affects their behavior in different environments. For instance, polar molecules can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, making them hydrophilic (water-loving). In contrast, nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic (water-hating) and tend to aggregate together.
Interactions between Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
Polar and nonpolar molecules interact differently due to their varying polarities. Polar molecules can form hydrogen bonds and dipole-dipole interactions, while nonpolar molecules primarily experience van der Waals forces.
Hydrogen bonding is the strongest intermolecular force and occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. Dipole-dipole interactions occur between polar molecules with permanent dipole moments.
Van der Waals forces are weaker intermolecular forces that include London dispersion forces and permanent dipole-induced dipole interactions. These forces are present in both polar and nonpolar molecules.
Applications of Polar and Nonpolar Molecules: Polar And Nonpolar Molecules Pogil Answers
The polarity of molecules has numerous applications in various fields:
- Pharmaceuticals:Polar molecules are often used as drug molecules due to their ability to interact with polar biological molecules.
- Materials Science:Nonpolar molecules are used in the production of hydrophobic materials, such as coatings and adhesives.
- Biotechnology:Polarity plays a crucial role in protein folding and enzyme activity.
Examples and Case Studies
Water:A polar molecule that is essential for life on Earth. Its polarity allows it to dissolve a wide range of polar and ionic compounds.
Oil:A nonpolar molecule that is insoluble in water. Its nonpolarity makes it useful as a lubricant and fuel.
Case Study: Drug Delivery:Polar drugs can be encapsulated in liposomes, which are small vesicles made of phospholipids. The polar head groups of the phospholipids interact with the polar drug molecules, while the nonpolar tails interact with the nonpolar environment outside the liposome. This allows polar drugs to be delivered to specific target cells.
FAQ Compilation
What is the key difference between polar and nonpolar molecules?
Polar molecules have a separation of charge, resulting in a net dipole moment, while nonpolar molecules do not.
How does polarity affect the solubility of molecules?
Polar molecules tend to be more soluble in polar solvents, while nonpolar molecules are more soluble in nonpolar solvents.
What are the different types of intermolecular forces that can exist between polar and nonpolar molecules?
Polar molecules can engage in hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions, while nonpolar molecules primarily exhibit van der Waals forces.