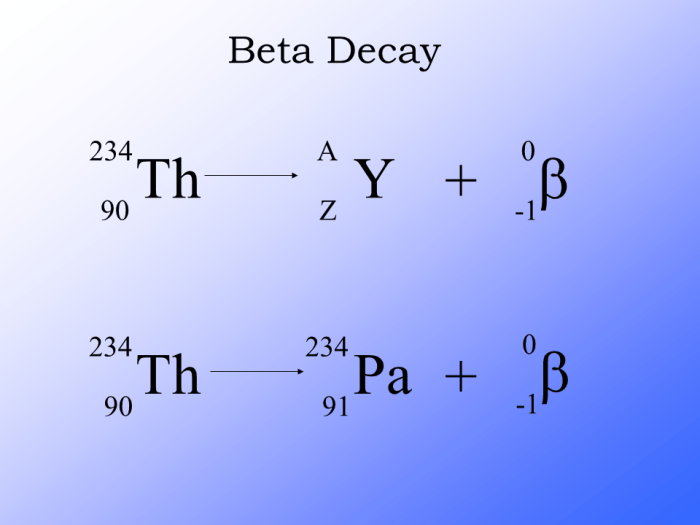The process by which a neutron becomes a proton crossword unveils the captivating realm of nuclear physics, where the transformation of particles holds the key to understanding the fundamental forces that govern our universe. This journey begins with the exploration of neutron decay, a process that reveals the intricate interplay between energy conservation and the weak force.
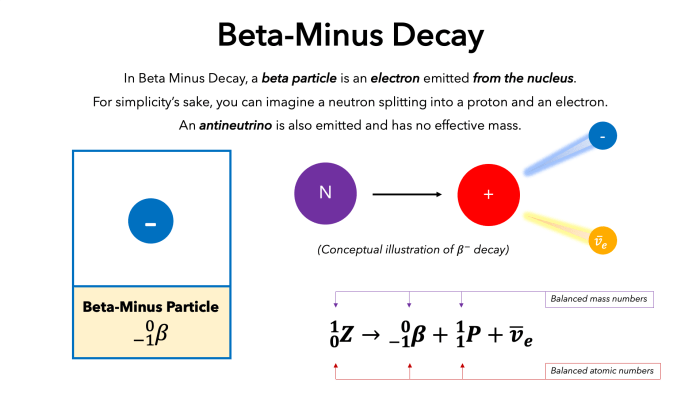
Neutron decay, a phenomenon that lies at the heart of this transformation, is a captivating dance of particles, where a neutron gracefully transitions into a proton, releasing a torrent of energy in its wake. The weak force, the enigmatic choreographer of this dance, orchestrates the emission of an electron and an antineutrino, setting the stage for the neutron’s metamorphosis into a proton.
Definition of Neutron Decay
Neutron decay is the process by which a neutron, a subatomic particle with no net electric charge, transforms into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. This transformation is mediated by the weak force, one of the four fundamental forces in nature.
Energy Conservation in Neutron Decay, Process by which a neutron becomes a proton crossword
The mass difference between a neutron and a proton is released as energy during neutron decay. This energy release can be calculated using the equation E = Δmc², where E is the energy released, Δm is the mass difference between the neutron and the proton, and c is the speed of light.
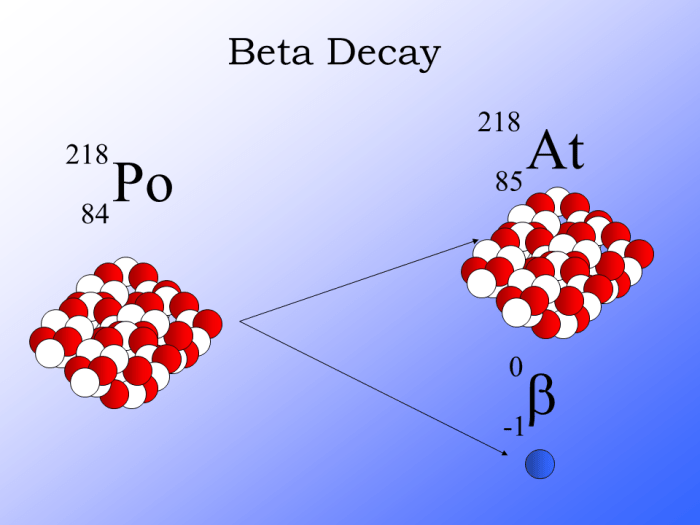
Beta Decay as a Process of Neutron Transformation
Neutron decay occurs through a process known as beta decay. In beta decay, the neutron decays into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. The proton remains in the nucleus, while the electron is emitted as beta radiation. The antineutrino is a particle with no mass or electric charge.
Detection and Measurement of Neutron Decay
Neutron decay can be detected and measured using various experimental techniques. One common technique is the use of a neutron detector, which is a device that detects the presence of neutrons. Another technique is the use of a bubble chamber, which allows researchers to observe the tracks of particles produced in neutron decay.
Applications of Neutron Decay
Neutron decay has a wide range of applications, including nuclear reactors and particle accelerators. In nuclear reactors, neutron decay is used to control the rate of nuclear reactions. In particle accelerators, neutron decay is used to study the properties of subatomic particles.
Expert Answers: Process By Which A Neutron Becomes A Proton Crossword
What is the role of the weak force in neutron decay?
The weak force is responsible for mediating the transformation of a neutron into a proton, electron, and antineutrino.
How is energy released during neutron decay?
The mass difference between a neutron and a proton is released as energy, which can be calculated using the equation E=mc^2.
What are the applications of neutron decay?
Neutron decay finds applications in nuclear reactors, where it contributes to the production of energy, and in particle accelerators, where it aids in the study of fundamental particles.